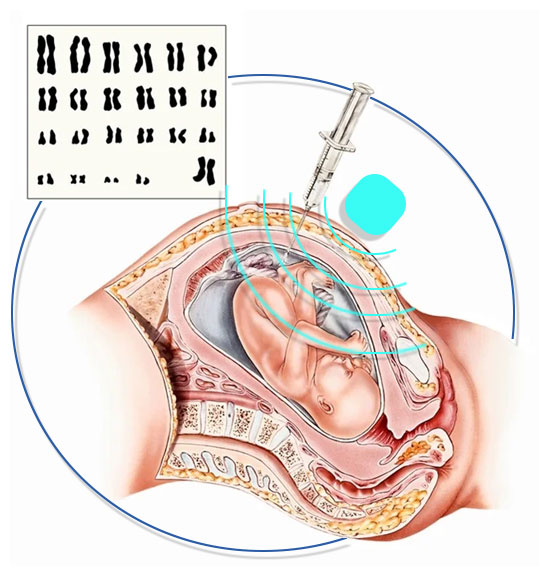
Why Should Amniocentesis be Performed?
AFT is a procedure for the diagnosis of chromosomal and genetic diseases and infections in the fetus. The procedure is usually performed between 16 and 24 weeks of gestation. It is very unlikely to produce results before 15 weeks of gestation, and after 24 weeks of gestation, cordocentesis is preferred and produces results much more quickly.
At AFT, the cells in the amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus are examined. Since these cells in the amniotic fluid come from the baby, the chromosomes in these cells also come from the fetus.
How is amniocentesis performed?
At AFT, a sample is taken from the amniotic fluid that does not contain the fetus (about 20 ml, at a rate of 1 ml/week) by piercing the abdominal wall and uterus of the expectant mother with a thin needle under sterile conditions and under ultrasound control, without touching the baby. This fluid is drawn up into a syringe and the sample is sent to the genetics laboratory. The procedure is very short and does not require anesthesia or antibiotics. Since most of the amniotic fluid is fetal urine, the amniotic fluid will return to its original amount within a few hours as the baby urinates, despite the sample taken. The procedure is terminated after the fetal heartbeat is checked.
What Can Happen After Amniocentesis?
In the first few days, you may experience groin pain or light bleeding. Usually, pregnancies are uneventful, and acetaminophen-based pain relievers may help. However, if you have excessive pain or bleeding or your temperature rises, return to the clinic immediately.
The rate of pregnancy loss due to AFT is much lower, about 0.12 percent (1 in 800 procedures). The cause may be leakage of amniotic fluid through the hole in the gestational sac, infections that may occur after the procedure due to the spread of microbes in the uterus, or bleeding.
The results of the tests are available after about 20 days, but FISH and qfPCR can also be used to screen for the five chromosomes (chromosomes 13, 18, 21, X, Y) with most abnormalities in the first few days. The reason why classical screening takes 20 days is because the cells are placed in culture medium and allowed to divide. Theoretically, the accuracy of the result is 100% and errors in the laboratory are rare. Sometimes the procedure has to be repeated because the cells do not grow in culture.